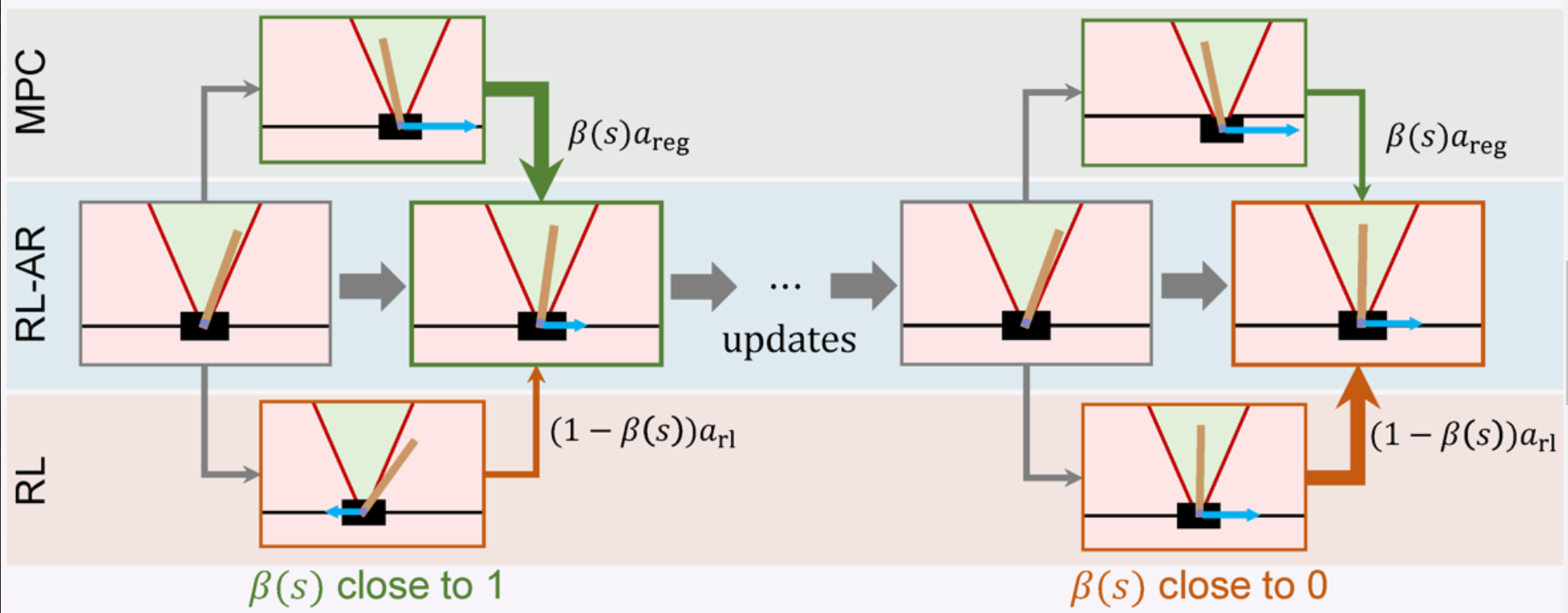
Reinforcement Learning with Adaptive Regularization for Safe Control of Critical Systems
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a powerful method for controlling dynamic systems, but its learning mechanism can lead to unpredictable actions that undermine the safety of critical systems. Here, we propose RL with Adaptive Regularization (RL-AR), an algorithm that enables safe RL exploration by combining the RL policy with a policy regularizer that hard-codes the safety constraints. RL-AR performs policy combination via a "focus module," which determines the appropriate combination depending on the state—relying more on the safe policy regularizer for less-exploited states while allowing unbiased convergence for well-exploited states. In a series of critical control applications, we demonstrate that RL-AR not only ensures safety during training but also achieves a return competitive with the standards of model-free RL that disregards safety.
Publication:
- Haozhe Tian, Homayoun Hamedmoghadam, Robert Shorten, and Pietro Ferraro. Reinforcement Learning with Adaptive Regularization for Safe Control of Critical Systems. In NeurIPS 2024.
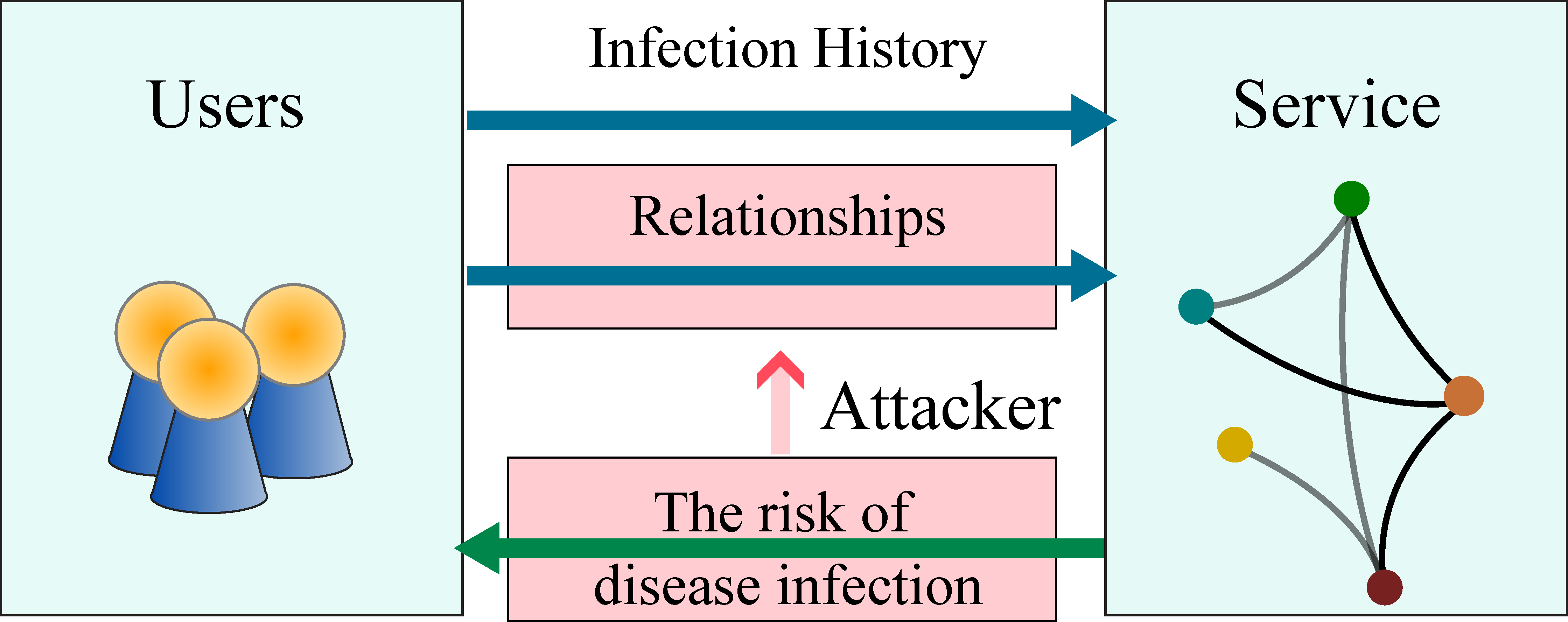
Link Inference Attacks in Graph Neural Networks
Graph Neural Network (GNN) is a widely-used machine learning model on graph data. However, GNN's potential leakage of sensitive graph node relationships (i.e., links) could cause severe user privacy infringements. Such attacks are named graph link inference attacks. This work considers the setting where some malicious nodes are established by the attacker. The added malicious nodes significantly enhance the practicality of link inference attacks. This work further proposes centroid-guided graph poisoning (CGP). Without participating in the training process of the target model, CGP operates on links between malicious nodes to make the target model more vulnerable to graph link inference attacks.
Publication:
- Haozhe Tian, Haibo Hu, and Qingqing Ye. CGP: Centroid-guided Graph Poisoning for Link Inference Attacks in Graph Neural Networks. In IEEE BigData 2023.
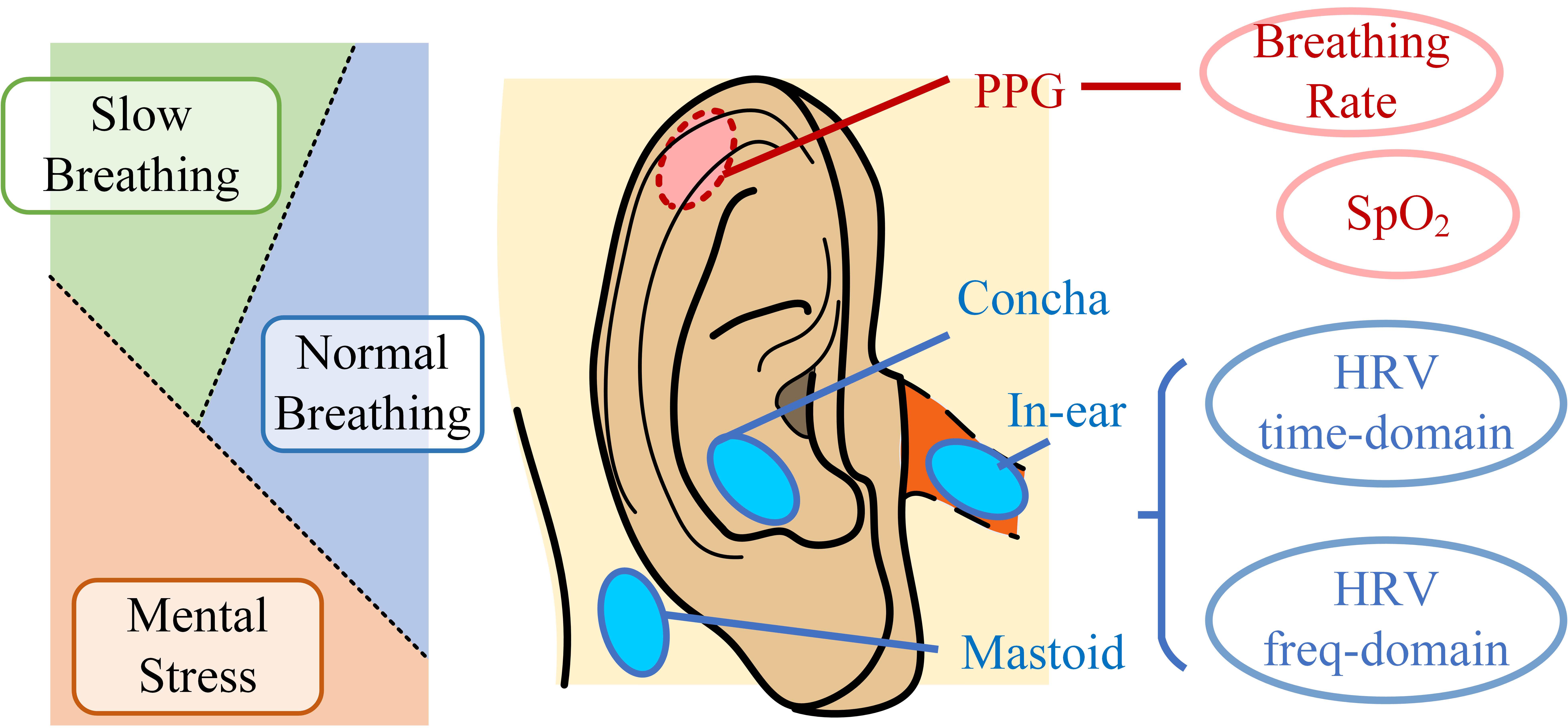
Physical State Classification using Ear-ECG and Ear-PPG
This work aimed to classifify three physical states using ECG and PPG measured around the ears. Ear-ECG and Ear-PPG contain less motion artefacts, and do not hinder subjects' movements. These advantages make ear measurements ideal for the monitoring of physical states. To classify physical states, time- and frequency-domain HRV features were extracted. To help distinguishing slow breathing, breathing intervals and SpO2 were extracted from PPG. It was proven that PPG features improved classification accuracy (95% cross-validation accuracy). New method based on automatically pre-trained matched filter was also used to extract low SNR Ear-ECG peaks.
Publication:
- Haozhe Tian, Edoardo Occhipinti, Amir Nassibi, Danilo Mandic, 2023, July. Hearables: Heart Rate Variability from Ear Electrocardiogram and Ear Photoplethysmogram (Ear-ECG and Ear-PPG). In IEEE EMBC 2023.
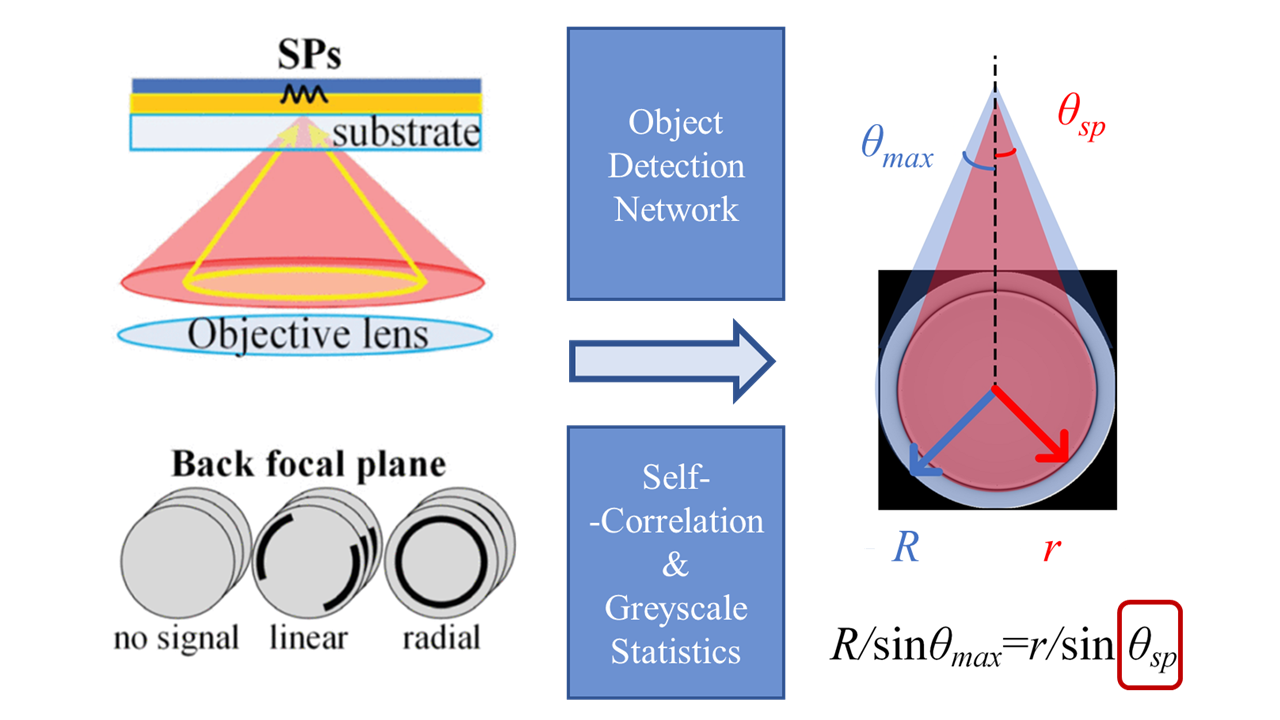
Automatic Surface Plasmon Microscopy based on Object Detection Network
Surface Plasmon Microscopy (SPM) features both high sensitivity and resolution. This work aimed to automatically conduct SPM measurements on batches of images. To do this, object detection networks (Faster R-CNN, SSD, YOLO) were used to classify and localize surface plasmon profiles. Self-correlation was also proposed to identify the center of surface plasmon profiles.
Publications:
- Bei Zhang, Haozhe Tian, Tianyu Xiao, and Jing Zhang. "Instrumentation of surface plasmon microscopy: complete scheme of signal extractions." In IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 70 (2021).



